Internal Ear Biology Definition. Noun internal ear the part of the ear that consists of the cochlea vestibule and semicircular canals 0. The portion of the ear consisting of the cochlea the vestibule and the bony semicircular canals which contain the receptors for static and dynamic equilibrium.
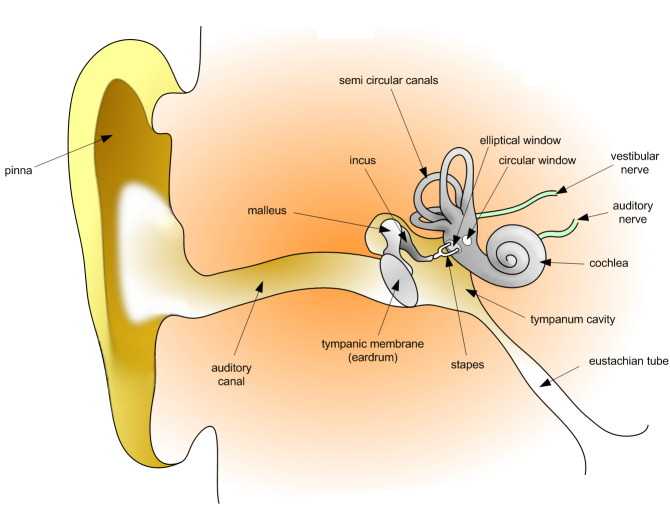
Oval window - connects the middle ear with the inner ear. The osseous labyrinth a series of cavities within the petrous part of the temporal bone and the membranous labyrinth a series of. The bony labyrinth a cavity in the temporal bone is divided into three sections.
Noun internal ear the part of the ear that consists of the cochlea vestibule and semicircular canals 0.
Noun internal ear the part of the ear that consists of the cochlea vestibule and semicircular canals 0. The inner ear receives vibrations that have been amplified and transmitted from the ear canal and through the malleus incus and stapes. The internal ear is the essential part of the organ of hearing receiving the ultimate distribution of the auditory nerve. Inner ear or labyrinth Collins English Dictionary Complete and Unabridged 12th Edition 2014 HarperCollins Publishers 1991 1994 1998 2000 2003 2006 2007 2009 2011 2014.